[Data Structure] Linked List
🧩 Linked List
Linked List & Array
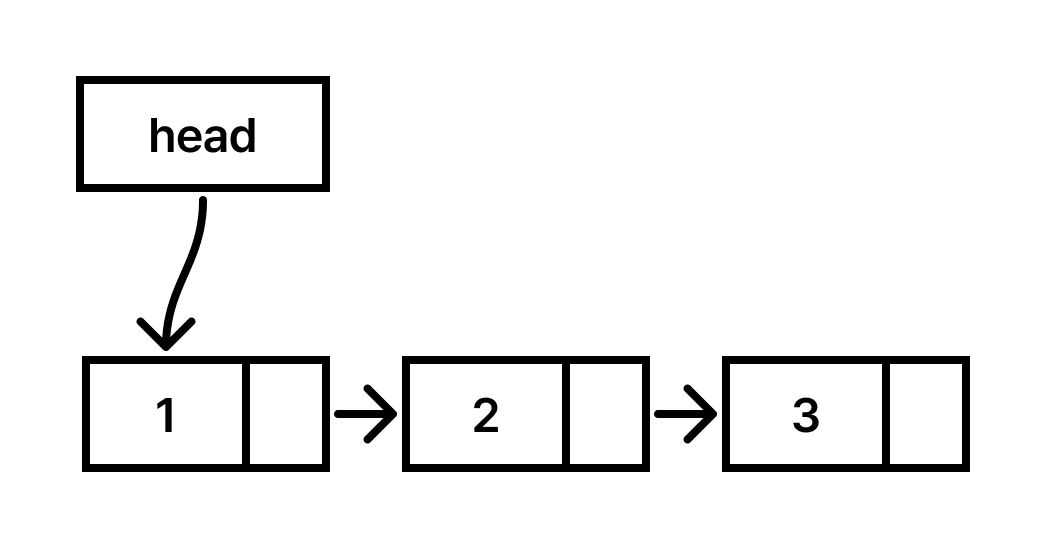
연결 리스트는 임의의 메모리 공간에 있는 요소를 연결하여 저장하는 자료구조입니다. 배열과의 비교를 통해 연결 리스트를 더 쉽게 이해할 수 있습니다.
배열은 연속된 공간에 요소를 저장합니다. C에서 다음과 같이 선언할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
int scores[100];
scores[0] = 1;
scores[1] = 2;
scores[2] = 3;
...
scores 내 각 요소는 자체 메모리 공간을 갖습니다. 모든 요소는 [] 연산자를 통해 편리하고 빠르게 접근할 수 있습니다.
하지만 배열은 컴파일 시점에 크기를 지정해야 하기 때문에, 계속해서 요소를 추가해야 하는 런타임 환경에서는 적절하지 않습니다. 이러한 단점은 동적 할당을 통해 어느정도 극복할 수 있지만 재할당 비용 및 메모리 낭비라는 문제가 여전히 존재합니다. 연결 리스트를 이용하면 이 문제를 완벽하게 해결할 수 있습니다.
Structure
연결 리스트는 노드(Node)라는 단위를 사용하여 요소를 저장합니다. Node는 data와 next로 구성되어 있습니다. next는 다음 Node 객체 자체를 가리키는 참조입니다.
1
2
3
4
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
Iteration & Length
리스트의 가장 기초적인 연산은 첫 노드(head)부터 끝(None)까지 훑는 겁니다. 여기서 중요한 원칙은 head라는 기준점(포인터)을 절대 잃어버리면 안 된다는 겁니다.
current 포인터를 사용한 패턴
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
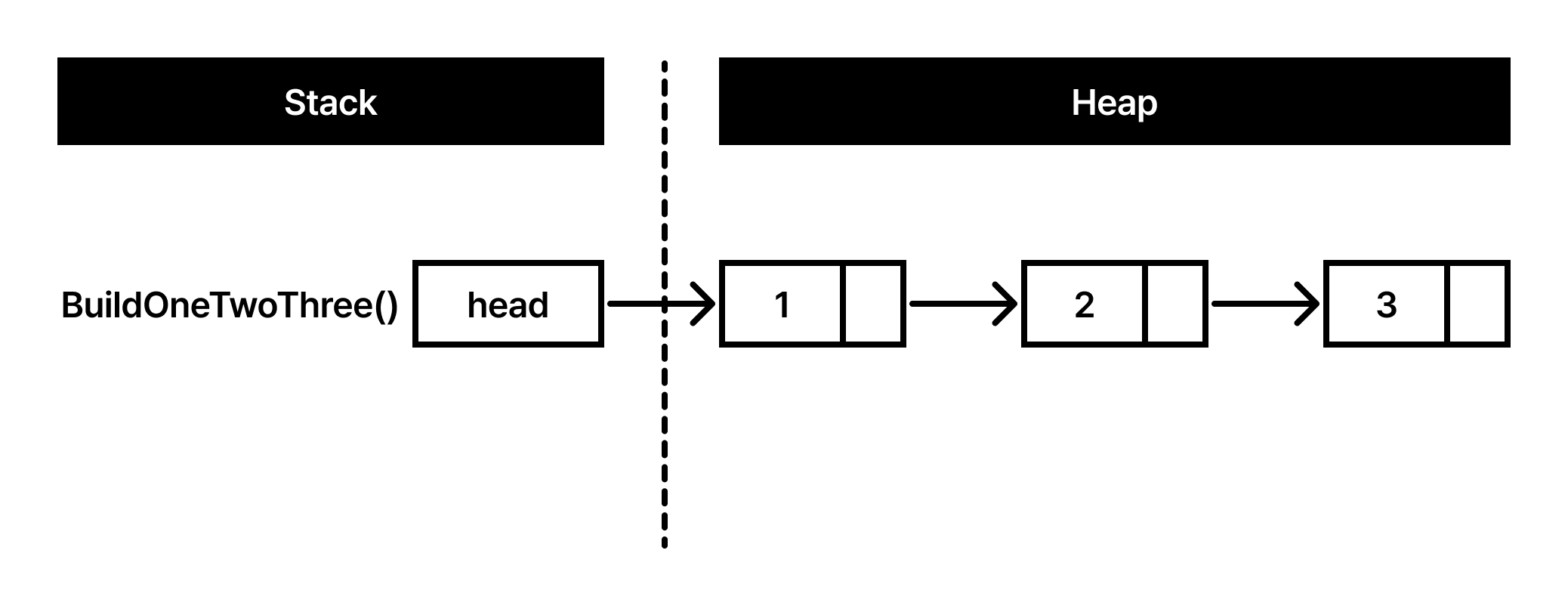
def build_one_two_three():
head = Node(1)
second = Node(2)
third = Node(3)
head.next = second
second.next = third
return head
def length(head):
current = head
count = 0
while current != None:
count += 1
current = current.next
return count
head = build_one_two_three()
print(length(head)) # 3
head를 직접 움직이지 않고, current를 지연 변수에 복사해서 움직이는 게 핵심입니다. 이 패턴은 데이터를 찾거나, 출력하거나, 수정하는 모든 로직의 기본이 됩니다.
current = current.next를 잊어버리면 무한 루프에 빠질 수 있으니 주의합니다.
🧩 Programming Philosophy
작동하지 않는 Push
기술적 관점에서 C에서 리스트 구축 시 리스트의 맨 앞에 데이터를 추가할 때 흔히 겪는 실수가 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void WrongPush(struct node* head, int data) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
int main() {
struct node* head = BuildTwoThree();
printf("%d\n", head->data); // 2
WrongPush(head, 1);
printf("%d\n", head->data); // 2
return 0;
}
함수에서 head를 바꿔도, 함수 밖의 원본 head가 바뀌지는 않습니다. WrongPush()의 head는 main()의 head와 별도의 스택 공간에 위치하기 때문이죠.
Sol 1. 명시적 반환 사용 (Functional Approach)
이중 포인터를 사용하여 포인터에 대한 역참조 연산을 통해 원본 포인터에 접근할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
void Push(struct node** headRef, int data) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *headRef;
*headRef = newNode;
}
int main() {
struct node* head = BuildTwoThree();
printf("%d\n", head->data); // 2
Push(&head, 1);
printf("%d\n", head->data); // 1
return 0;
}
파이썬에서는 이중 포인터(**)를 사용해 외부 변수를 직접 수정하는 게 불가능합니다. 대신, 변경된 head를 반환하고 밖에서 다시 받아 해결할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def push(head, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = head
return new_node
head = None
head = push(head, 1)
head = push(head, 2)
print(length(head)) # 2
Sol 2. Wrapper Class 사용 (OOP Approach)
head를 클래스로 감싸서 관리하면, head는 클래스의 멤버 변수로서 힙 공간에 위치하기 때문에 수정이 자유로워집니다. 실무에서는 이 방법이 더 권장됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
ll = LinkedList()
ll.push(1)
ll.push(2)
print(ll.head.data) # 2
Implementation Strategies
A. Head에 추가하기 (Stack)
앞서 본 push를 계속 호출하는 방식입니다. 코드는 간단하지만, 데이터가 역순으로 저장됩니다. 예를 들어, 1, 2, 3 순으로 입력하면 3, 2, 1 순으로 저장됩니다.
B. Tail 포인터와 특수 케이스 (Queue)
순서를 지키려면 뒤쪽에 붙여야 합니다. 매번 끝까지 찾아가지 않으려면 마지막 노드를 가리키는 tail 포인터를 유지해야 합니다.
하지만 여기엔 치명적인 단점이 있는데, “첫 번째 노드일 때”와 “그 이후일 때”의 코드가 다릅니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
def build_with_tail_pointer():
head = None
tail = None
for i in range(1, 6):
new_node = Node(i)
if head is None:
head = new_node
tail = new_node
else:
tail.next = new_node
tail = tail.next
return head
head = build_with_tail_pointer()
print(head.data) # 1
케이스를 별도로 처리한다는 점에서 조금 아쉬운 전략입니다.
C. Dummy Node (가장 우아한 해결책)
빈 껍데기 노드(Dummy)를 하나 만들고 시작하면, head가 None인지 검사할 필요가 없습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def build_with_dummy_node():
dummy = Node("DUMMY")
tail = dummy
for i in range(1, 6):
tail.next = Node(i)
tail = tail.next
return dummy.next
head = build_with_dummy_node()
print(head.data) # 1
이 방식은 “모든 노드는 앞 노드의 next에 붙는다” 는 규칙을 첫 번째 노드에도 강제로 적용시켜 코드를 단순화합니다.
Local Reference
더미 노드 없이 모든 노드를 동일하게 처리할 수 있는 C언어의 독특한 기법입니다. tail 노드를 가리키는 게 아니라, 마지막 링크(next 포인터 자체)의 주소를 가리킵니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
struct node* BuildWithLocalRef() {
struct node* head = NULL;
struct node** lastPtrRef = &head;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
Push(lastPtrRef, i);
lastPtrRef = &((*lastPtrRef)->next);
}
return head;
}
int main() {
struct node* head = BuildWithLocalRef();
printf("%d\n", head->data); // 1
return 0;
}
파이썬의 메모리 주소 조작 및 참조 제한
파이썬은 변수의 메모리 주소를 직접 조작하거나,
next필드 자체의 참조를 가져오는 기능이 없습니다.
Copy
Iterative + Dummy Node 활용
원본 리스트를 순회(current)하면서 새 리스트(new_list)를 만듭니다. 이 때 Dummy Node를 쓰면 코드가 매우 깔끔해집니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def copy_list(head):
current = head # 원본 순회용
dummy = Node(0) # 복사본을 위한 Dummy
tail = dummy # 복사본의 끝을 가리킴
while current is not None:
tail.next = Node(current.data)
tail = tail.next
current = current.next
return dummy.next
재귀적 접근 (Recursive)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
def copy_list_recursive(head):
if head is None:
return None
new_node = Node(head.data)
new_node.next = copy_list_recursive(head.next)
return new_node
파이썬의 재귀 한도와 리스트 크기 제약
리스트가 길면 파이썬의 재귀 한도(Recursion Limit)에 걸릴 수 있다는 점에 주의합니다.
Implementation in Java
1. Fields
first와 last는 실제 데이터가 아닌 Dummy 역할만 수행합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
private int size = 0;
private final Node<E> first;
private final Node<E> last;
public MyLinkedList() {
first = new Node<>(null, null, null);
last = new Node<>(first, null, null);
first.next = last;
}
}
2. Inner Class
이전 노드를 가리키는 prev를 추가하여 이중 연결 구조를 가집니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
3. Methods
linkLast(), linkBefore()
linkLast()는 리스트의 가장 뒤에 노드를 추가(append)하고, linkBefore()는 특정 노드(succ)의 앞에 삽입(insert)합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
void linkLast(E e) {
linkBefore(e, last);
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
}
}
unlink()
노드 x를 삭제(unlink)합니다. GC 효율을 위해 내부 참조를 모두 null로 지웁니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
x.item = null;
x.prev = null;
x.next = null;
size--;
return element;
}
}
node()
인덱스가 절반보다 앞이면 앞에서, 뒤면 뒤에서 탐색합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < size / 2) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
return x;
}
}
}
만약 Dummy Node가 없다면?
각 메서드에 불필요한 null 체크가 발생합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null) {
first = newNode;
} else {
l.next = newNode;
}
size++;
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null) {
first = newNode;
} else {
pred.next = newNode;
}
size++;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = next;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
return element;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < size / 2) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
return x;
}
}
}
4. 공개 API (Public Methods)
add()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size) {
linkLast(element);
} else {
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
}
}
get()
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
}
remove()
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
}
size()
1
2
3
4
5
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
toString()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
Node<E> curr = first.next;
while (curr != last) {
sb.append(curr.item);
if (curr.next != last) sb.append(", ");
curr = curr.next;
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
Helpers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class MyLinkedList<E> implements Iterable<E> {
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
}
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
}
5. Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>();
// 1. 추가
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
System.out.println("기본 추가: " + list); // [10, 20, 30]
// 2. 중간 삽입
list.add(1, 15);
System.out.println("중간 삽입: " + list); // [10, 15, 20, 30]
// 3. 삭제
list.remove(2);
System.out.println("삭제 후: " + list); // [10, 15, 30]
// 4. 이터레이터 순회
System.out.print("순회: ");
for (Integer i : list) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
여기에서 전체 코드를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Summary
연결 리스트를 다룰 때, 다음 3가지 프로그래밍 철학이 중요합니다.
- Memory Model: 변수는 객체를 가리키는 참조입니다.
- Pointer Manipulation:
current같은 임시 포인터를 적극적으로 활용합니다. - Dummy Node:
if head is None같은 지저분한 코드를 없애는 최고의 패턴으로 활용합니다.